“I can’t believe we made it,” sings Beyoncé in “APES**T,” the first single from her surprise joint album with Jay-Z, Everything Is Love. And to prove that she and her husband have made it, in the song’s accompanying video, Beyoncé delivers this line from the Louvre.
As the New York Times has pointed out, it is not actually that expensive to shoot a video in the Louvre (about $17,500 for a full day’s shoot). But music videos aren’t about numbers; they’re about how things feel — and there’s no place on earth that feels as lavish, as rich with accumulated cultural power and wealth and colonialism, as the Louvre. If you want to show that you have made it, that you are rich and powerful and one of the greatest artists of your generation, you go to the Louvre.
And as an artistic choice, the Louvre is par for Beyoncé’s course. For the past few years, Beyonce has increasingly cribbed from the iconography of classical Western art in her own image-making. Her pregnancy announcement photo shoot and her birth announcement photo shoot both referenced Botticelli’s Venus and the Renaissance trope of the Madonna and child, and her 2017 Grammys performance drew on goddess imagery from multiple artistic traditions.
So when Beyoncé shoots at the Louvre — taking on by turns the poses of Venus de Milo and Victory — she’s continuing an artistic project of recontextualizing classical Western art, of making herself the aesthetic object on which so much wealth and cultural capital has been spent. And coming from a black woman, that’s a radical statement.
“In a way, Beyoncé is exploiting/marketing her blackness as creativity — as a kind of weapon — within and against the very Eurocentric system of culture and consumption from which she has benefited,” says James Smalls, a professor of art history at the University of Maryland Baltimore County.
That’s an especially radical statement to make in the context of the Louvre, where little of the art features people of color in positions of strength and power. “From the Middle Ages up to the 19th century, works of art that showed black people usually represented them as servants or secondary figures,” explains Smalls. “They were not deemed worthy subjects of paintings, sculptures, or other kinds of cultural works.”
One of the few exceptions to that trend is Marie Benoist’s “Portrait d’une négresse,” also displayed at the Louvre. “That painting is an anomaly because it presents a black person as the sole aestheticized subject and object of a work of art,” Smalls says. And it’s the painting that appears at the end of the “Apeshit” video, after shot after shot of portraits of white people.

Benoist painted “Portrait” in 1800, during a brief period in which France had abolished colonial slavery. (In 1794, the French emancipation proclamation liberated the colonies; in 1802, Napoleon reinstated slavery.) In that six-year span, portraits of heroic black people became popular in France, and that created an opportunity for an image of a black woman who is not tending to or subordinate to a white person, who is instead considered worthy of being at the center of her own portrait.
As Smalls has pointed out, in its full context, “Portrait” is not a wildly politically subversive image. It’s most likely that the unknown and unnamed subject was a servant with few legal rights who had little choice about how she posed or whether she was okay with her breast being exposed to the world for the next 200 years. Benoist the painter has much more agency here than the black woman at the center of the picture.
But in the context of “Apeshit,” with its montages of painting after painting of white faces and white statues, “Portrait” feels both shocking and subversive. It’s a black face in the center of the frame, apparently in control of her domain. And it’s one of the only figures in the Louvre that we don’t see get reinterpreted by either the Carters or their dancers: The only figure in the Louvre that can withstand the unstoppable force that is Beyoncé, that does not need to be remade and reexamined.
Part of Beyoncé’s project over the past few years has been to treat art as a form of power: It is a form of focused aesthetic attention, of social capital, and of wealth given solid form. Taking over the Louvre means taking all that power for herself and for the black bodies she brings in with her — except for the “Portrait.” In “Apeshit,” it can stand on its own.
What do Beyoncé, The Smurfs 2, and you have in common? All three have the theoretical ability to rent out the Louvre. Though there was widespread awe that the Carters’ video for “Apeshit” took place inside the most famous museum in the world, turns out, it’s actually not all that uncommon.
According to the New York Times, about 500 shoots take place at the Louvre each year, which have included films on opposite ends of the “is this a good movie” spectrum, from last year’s Wonder Woman to 2013’s The Smurfs 2, which even the Louvre couldn’t save from its 13 percent Rotten Tomatoes rating. Though the museum only allows photography in the galleries for private use, it makes exceptions for professionals through written authorization.
As of 2015, the Louvre’s policy states that to shoot a short film or music video, the cost for both interior and exterior shots would be just €4,500, or about $5,200. It’s possible that if the Carters had a crew of more than 50 people, that number would have been closer to €18,000, but as the Times notes, “there are hotel rooms here that cost more than that.”
Hosting private events, however, will cost you a bit more. A tour for under 50 guests will set you back €10,000, while renting out the reception hall beneath I.M. Pei’s pyramid will cost, at the very least, €28,000. Though, to reiterate, that isn’t an amount at which anyone would gasp, “Mon dieu!”
Lorde, I have an idea for you about where to film your video for “The Louvre.” Call me!
In the video for Beyoncé and Shawn Carter‘s “Apeshit,” the first visual from the pair’s surprise joint album Everything Is Love, the two stars romp through the Louvre in Paris, seizing center stage in a high-culture palace that – like most Western art museums – historically made little room for non-white artists.
Some of their mission involves the strategic highlighting of non-white images already in the Louvre. Beyoncé and Jay-Z rap in front of an Egyptian sphinx, and in galleries filled mostly with neo-classical French paintings – white artists, white subjects – the camera singles out black faces. (The video is directed by Ricky Saiz, who also helmed the “Yonce” video from Beyoncé Knowles-Carter’s eponymous 2013 album.) Viewers catch brief glimpses of a pair of black figures in Paolo Veronese’s painting “The Wedding at Cana,” where Jesus turned water into wine, as well as a quick look at Marie-Guillemine Benoist’s “Portrait d’une Négresse,” a depiction of a black woman staring guilelessly back at the viewer.
But the Where’s Waldo? moments highlighting black figures are fleeting – the possibilities for this in the Louvre, or any major Western art museum, are limited from the start. So Beyoncé and Jay Z set about interjecting blackness into a space that has never placed much value on it, claiming one of the centerpieces of European culture with gleeful defiance. They frequently film themselves moving in opposition to the frozen stillness of paintings by Jacques-Louis David, a French neoclassical artist whose work – like “The Oath of the Horatii” and “Madame Récamier” – invokes the Greco-Roman tradition.
Much of the potency of the “Apeshit” video comes from the contrasts drawn between the “white” art on the walls and the black women on the gallery floors. In front of David’s “The Consecration of the Emperor Napoleon and the Coronation of Empress Joséphine,” a court scene of relentless white extravagance, Beyoncé and eight black dancers hold hands and begin to dance. It takes just a few synchronized sashays to upstage David’s massive painting, replacing an ornate symbol of white authority with a celebration of black bodies in motion. The Louvre’s stature depends on people believing that “The Coronation of Empress Joséphine” is the art, but the eye tells a different story – hanging behind Beyoncé and her dancers, the painting is reduced to wallpaper.
Throughout the “Apeshit” video, Beyoncé and Jay-Z repeatedly upstage some of Western classical art’s most famous images in one of its central sacred spaces. Beyoncé holds a series of chopping micro-poses with her hands before Saiz cuts quickly to an image of a distressed character, hands held up to shield her head, taken from another David painting, “The Rape of the Sabine Women.” The placement of the hands connects the two frames, but Beyoncé’s is virile, aggressive and in charge, while David’s figure seems merely fearful.

Radical gestures roll in on a mightily slippery sliding scale these days, don’t they? We’re far past any cultural division between high and low or pop and art at this point, and artists on the charts are also sniffing out their next inspiration, album cycle, or comparison to their own personal affairs in the grander schemes of culture and history. You’d be hard pressed to find a more hallowed repository of the West than the Louvre, so of course that’s where Beyoncé and Jay-Z have rolled up to set their new music video for the track “Apeshit” from the fresh album they dropped like an anvil right on top of your weekend.
Of course this isn’t the first time they’ve been there, nor the first time some Pop-ish upstarts made a Major Statement at the French museum, but it would seem to be a major escalation in the Carters x Louvre relationship, to say nothing of the pride re: their own marital ties that the album and video are so keen to showcase. When worlds (and genres) collide is still a strong trend across multiple spheres of art and culture—turning meaning and message into something of a competitive game of Russian nesting dolls or an arms race of spectacle-based oneupmanship—but what might we make of this night at the museum if considered in light of the 1960s Marxist avant-garde French Situationist International?
Founded in 1957 by Guy “Barrel of Laughs” Debord and Asger “Beware the Palette Knife” Jorn, the Situationists were guys and gals, but mostly guys, who wanted to, as the name would indicate, create some situations and elevate to the level of philosophy the notion of taking a freaking walk outside. But they also had a strategy! And key among their techniques, to which you can probably attribute the rise of “culture jamming” and just whatever Banksy thinks he’s doing, was the détournement. Discussed in chapter 8 of Debord’s 1967 tract The Society of the Spectacle, the technique calls for taking advantage of existing cultural objects or canonized art, rerouting their message, and even advocates for theft: “Plagiarism is necessary. Progress depends on it. It sticks close to an author’s phrasing, exploits his expressions, deletes a false idea, replaces it with the right one.” You would not have wanted this guy for your editor, but if you were looking to smash the state (of meaning), Debord was your man.
So, if “détournement serves as a reminder that theory is nothing in itself, that it can realize itself only through historical action and through the historical correction that is its true allegiance,” then is the spectacle of “Apeshit” a glam, historical correction of the Western assumption that houses of European culture contain the highest achievements of man- and womynkind? Beyoncé and Jay-Z have more clout and pull at this point than a merely rich person or garden-variety aristocrat putzing around the Cotswolds or Monaco, and they built that for themselves. When they pull off a stunt like this, it feels like another chime in the prosperity gospel that Doreen St. Félix examined in the arc of Rihanna’s career, as well as further evidence that the ability to make a compelling spectacle of oneself, to write a personal narrative as large as that of the progress of a civilization, is success.
The false idea here is white supremacy, and perhaps the correction then is that European colonialists may not have had the time or the means to make their masterpieces if it weren’t for the economic boon of slavery and historical pillaging of resources from southern and eastern continents for the benefit of countries like France. The Situationists didn’t really like spectacle much (“The spectacle in general, as the concrete inversion of life, is the autonomous movement of the non-living”) but they recognized that it was inescapable in modern society (“The spectacle is not a collection of images, but a social relation among people, mediated by images”).
Given this circumstance, Beyoncé and Jay-Z, god bless them, would appear to be doing their best to create a spectacle that people who look like them can see themselves in too, as opposed to the near uninterrupted stream of black death spectacle the media and world is awash in on a day to day basis. Look forward to hearing this jam blasting out of car speakers this summer—it’ll be a real situation.
The surprise release of Beyonce and Jay-Z’s new album, Everything Is Love, (credited as “The Carters” on the album to recognize they’re performing as a united duo, not as individuals) on Saturday, June 16 has left the music world reeling.
Already, what fans have been carefully dissecting – and what we’re interested in unpacking, too – is the imagery from the music video for the album’s lead single, “APESHIT”. The six-minute video is likely going to be considered one of the best of 2018, with The Carters and a troupe of dancers taking over the Louvre. In case you couldn’t already tell, the fact that Bey and JayZ even got unfettered access to the Louvre for their own use is a stunning power move – adding a glorious power to the “APESHIT” lyric “I can’t believe we made it/ This is why we’re thankful”.
Let’s start with the primary location in “Apeshit”: the Louvre. Historically, it’s a predominately white space that primarily features white, male-created works of art. It’s a microcosm of history, which itself is mostly white, male, and heterosexual. Tradition and the Louvre go hand-in-hand, too, which means that Beyoncé and Jay-Z’s presence is a total disruption from the beginning. For modern audiences and fans of The Carters, the disruption is surely welcome.
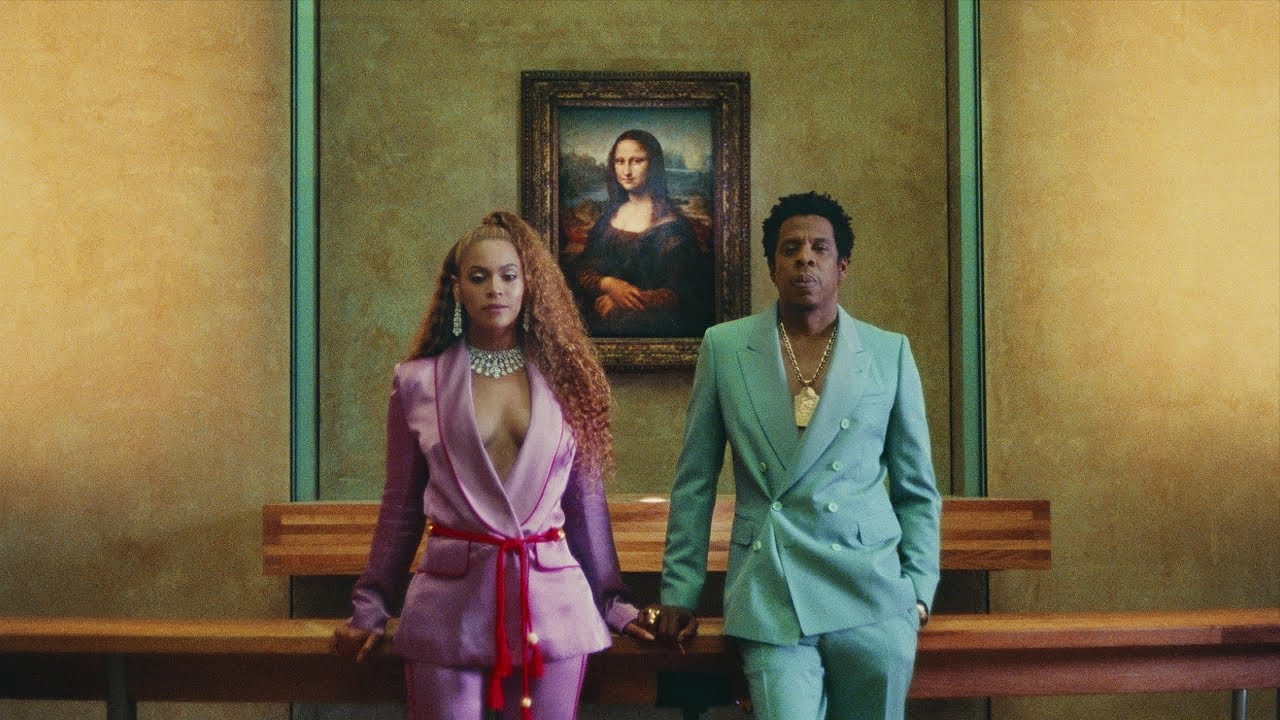
Not only can we expect to see (and do see) The Carters standing next to some of the most famous works of art, including the Mona Lisa and Winged Victory of Samothrace, but we see that they are aligning themselves with it right out of the gate. Their presence in a place that preserves what history has deemed the most important artworks, standing next to said art while themselves looking like art and using their body language to engage with this art, already implies they are as worthy of being there as the older work. It’s a middle finger to convention, a dare aimed at squarely at the gatekeepers of history and artistic tradition: You know we deserve to be here.
The Carters begin positioning themselves as iconography from the moment we first see them, standing in front of the “Mona Lisa”. Sure, it’s a callback to the first time they took a photo with arguably the most famous painting in history back in 2014, but something is different this time around.
Like the “Mona Lisa”, Beyoncé and Jay-Z are dressed simply, but powerfully. Suits for both, in bright colours and styles specific to their tastes and representative of the times they live in; again, just like the “Mona Lisa”. But even more of an echo of the painting is their expressions: a strong stare straight ahead, lips pressed together, shoulders back. They are telegraphing to us that they are as iconic as the “Mona Lisa”, without even saying a word. By donning expressions very much in the same vein as the iconic painting, they’re telling the viewer that they’re basically in the presence of a peer.
But even more than that, they’re commenting on the beguiling and enticing space they occupy in our own culture. Much like the “Mona Lisa”, they are telling us that they know we think about them in a way we don’t think about other music artists. They know that we’ll spend hours analysing them and their work, attempting to find meaning in their movements and lyrics, trying to work out the symbols and icons they’ve put forth, and hoping to crack the impenetrable fortress they’ve built around them (from which they only emerge to become vulnerable when they want to).
Humans have spent centuries trying to unpack the enigma of the “Mona Lisa” and still continue to do so to this day; do you really think you can figure out The Carters in a day?
Another immensely important moment from “APESHIT” comes in the repeated glimpses of Marie-Guillemine Benoist’s “Portrait of a Black Woman (Negress)” from 1800. One of the few works of art painted by a woman in the Louvre, the painting is deeply important both as a feature in the Louvre and its place in art history, because it is the only painting of its time to depict a black woman who is not a slave or similarly subjugated person, but rather simply presented in all her glory.
The painting affirms that black women are worthy of being in artistic spaces, and in enduring imagery. The painting is shown a few times, and it’s the second to last painting we see before the video closes on Bey and Jay turning around to regard the “Mona Lisa” – further confirmation that Benoist’s painting and its subject deserve recognition.
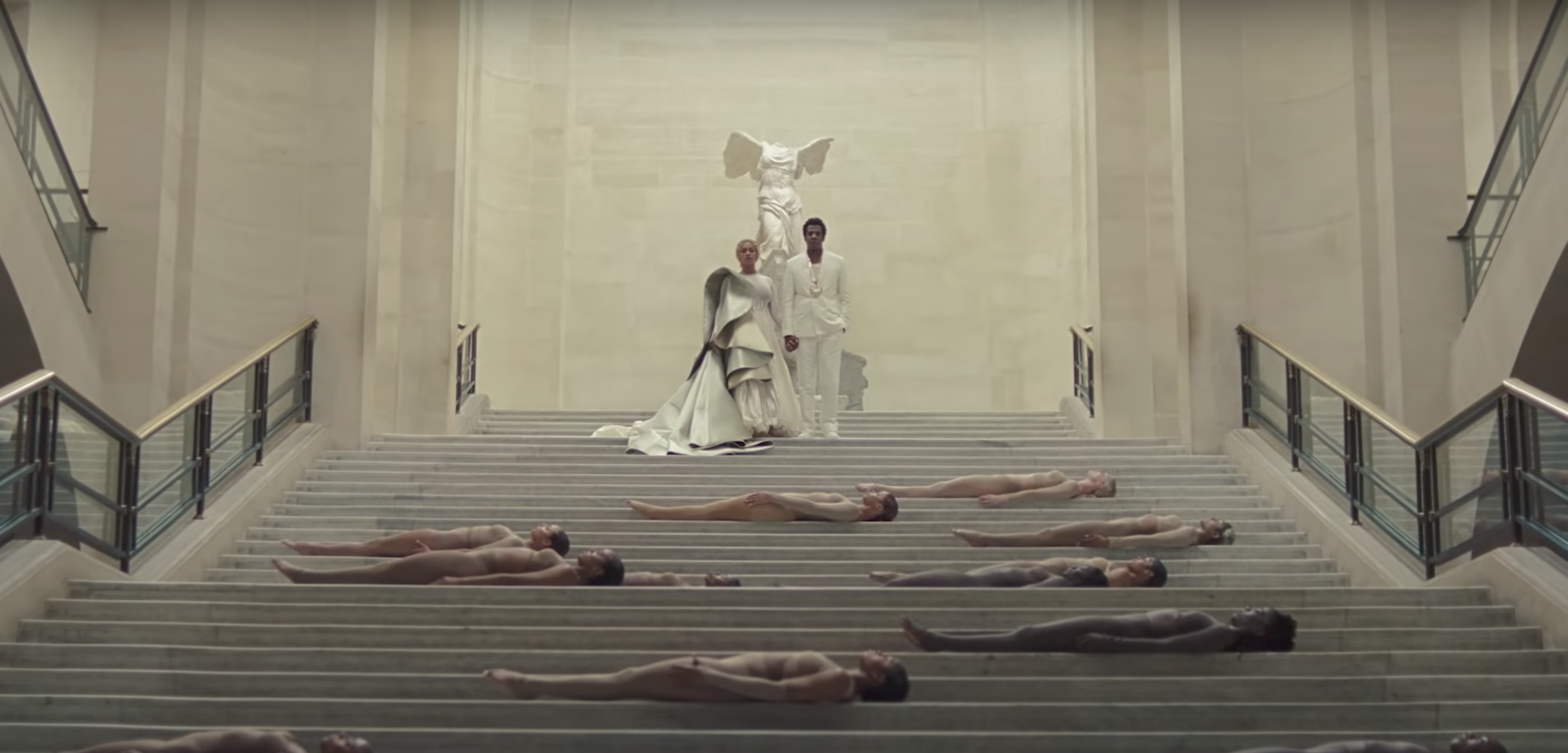
It’s also no accident that the “Winged Victory of Samothrace” statue is frequently seen in “APESHIT”. Implying triumph and power, the statue has endured over centuries, and The Carters imply just as much by once again standing in front of it, in perhaps a nod to their own triumph and the power they’ve achieved. According to the Louvre website for the piece, the statue depicts Nike, and was likely created to commemorate a naval victory by the Rhodians (who hail from Rhodes, part of the Dodecanese island group in Greece). The towering relic from the Hellenistic period is, as the Louvre’s description notes, intensely dramatic and glorifies the female body in connection with something traditionally masculine (victory in war).
That endowment of power to a female body is then emulated in the female bodies that stand before it in present day, through Beyoncé and her troupe of female dancers. All of these women come together and move as one being, with Beyoncé presiding over them all. She is the modern image of victory over the warfare placed on her body, career, intellect, personal life; having succeeded, she can now dress like “Winged Victory” and, in a sense, pass along her victories to the women who dance on the steps in front of her.
Twitter user Queen Curly Fry’s in-depth Twitter thread breaking down the art seen in “APES**T” is thorough, and her comments on the incorporation of the “Venus de Milo” into the video is so neatly articulated that we couldn’t have said it better if we tried: “Here, Beyoncé once again models herself as a Greek statue, this time the Venus de Milo. However, in this shot she wears a nude bodysuit with wrapped hair, reframing both goddesses of beauty and victory as a black woman. This dismantles white-centric ideals of beauty.”
Similarly, Twitter account Tabloid Art History nails why it’s so important and iconic for Beyoncé Knowles-Carter and her dancers to be dancing in front of “The Consecration of the Emperor Napoleon and the Coronation of Empress Joséphine” by Jacques Louis David from 1804: “What I especially like about this part of the video is that the painting itself depicts a disruption, Napoleon taking the Pope’s role from him and crowning Josephine himself. Beyoncé further disrupts this by taking on Josephine’s role as the one being crowned.”
If we consider Napoleon’s role as a major coloniser in the early 19th century, particularly in Northern Africa, then Beyoncé’s placement in the shot is extra symbolic. Beyoncé standing underneath the place where Napoleon is seen crowning his wife in the painting is a symbolic retrieval of stolen power.
One of the other paintings we see in “APESHIT” is another Jacques-Louis David painting, “The Intervention of the Sabine Women.” Interestingly, we only see portions of the painting, never the entire artwork. This could be a sly comment on the dissection and appropriation of black bodies by white culture for their own aesthetic uses – or it could just be a deft use of quick cuts for dramatic effect for the video. Or maybe it’s both.
Twitter user Queen Curly Fry notes here that the painting, for the puposes of “APESHIT”, depicts “(white) female fear evoked by (white) male violence is juxtaposed w/ (black) female empowerment (‘get off my dick’).” The painting’s use of white female tears –long criticised as a way for white women to shift any blame they deserve for racist behaviour, or to turn a blind eye to racial injustice – is in direct contrast with Beyonce and her dancers’ freedom, calm, and enlightenment.
In the end, “APESHIT” is a triumph because it is a statement that only The Carters could successfully make. The visual tells the powers that be to fuck off with their tradition, their preciously guarded history that has sought to erase non-white people from the history books, and their preconceived notions about how black bodies can be ornamental.
They’ve used art to push back, to demand honour for the work they’ve contributed. “APESHIT” is a force to be reckoned with, and The Carters’ use of art to make a statement is an announcement to the world that they’ve shaped culture as much as anything hanging on a gallery wall.
No comments:
Post a Comment